Temporal regularities shape perceptual decisions and striatal dopamine signals.
To optimize behaviour, animals and humans may learn about temporal regularities present in the environment. For example, a traffic light that recently turned green can be expected to remain green for a while. Conversely, a yellow traffic light can rapidly change to red, thus prompting a driver to decelerate. This paper presents experiments shedding light on how our brains learn about such temporal regularities to adjust behaviour appropriately.
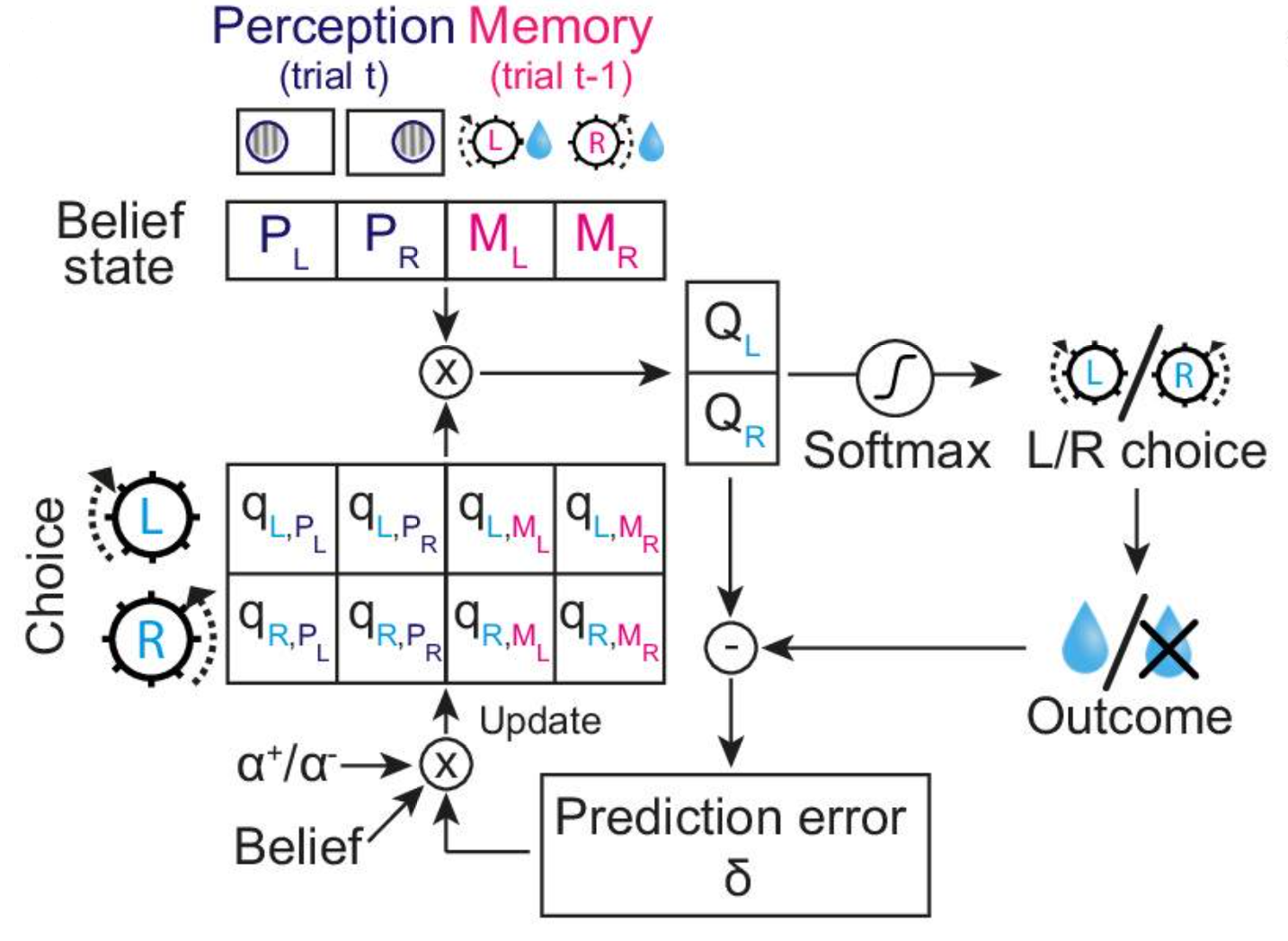
Perceptual decisions should depend on sensory evidence. However, such decisions are also influenced by past choices and outcomes. These choice history biases may reflect advantageous strategies to exploit temporal regularities of natural environments. However, it is unclear whether and how observers can adapt their choice history biases to different temporal regularities, to exploit the multitude of temporal correlations that exist in nature. Here, we show that male mice adapt their perceptual choice history biases to different temporal regularities of visual stimuli. This adaptation was slow, evolving over hundreds of trials across several days. It occurred alongside a fast non-adaptive choice history bias, limited to a few trials. Both fast and slow trial history effects are well captured by a normative reinforcement learning algorithm with multi-trial belief states, comprising both current trial sensory and previous trial memory states. We demonstrate that dorsal striatal dopamine tracks predictions of the model and behavior, suggesting that striatal dopamine reports reward predictions associated with adaptive choice history biases. Our results reveal the adaptive nature of perceptual choice history biases and shed light on their underlying computational principles and neural correlates.
2024. Nat Commun, 15(1):7093.
2024. PLoS Comput Biol, 20(4)e1011183.
